| Microsoft Research Shows How To Turn Any Camera Into A Depth Camera |
| Written by Mike James | |||
| Wednesday, 13 August 2014 | |||
|
It's SIGGRAPH so you expect a lot of amazing graphics, but Microsoft seems to cornering the market in wow. In this case, take any ordinary video camera and, with a small change, turn it into a really good depth camera. There are some limitations to what you can reliably detect, but more of this in a moment. The idea is that if you shine a light onto something then the amount of light scattered back depends on how far it is away. It also depends on lots of other factors, but this is the basic idea. What Microsoft Research has done is to take a standard video camera and remove its IR blocking filter and replace it with an IR band pass filter. Most cameras have an IR filter to stop infrared spoiling the video, but they are sensitive to infrared if you remove the filter. (The Raspberry Pi and some other video cameras are available with the IR filter removed just for special effects video creation). If you replace the filter with one that only passes infrared then you have a pure infrared camera. Now add some infrared LEDs and you have a device that can measure the amount of IR light an object reflects back and hence how far away it is.
As already mentioned, the big problem is how to calibrate the amount of light reflected back to the camera to get distance. In the past this has involved careful fixed setups that could be calibrated and then used. What the Microsoft team has done is use machine learning to find the depth of a single pixel as a joint function of the brightness of its surrounding pixels. Of course, the problem is that this function is going to vary according to the type of objects in the field of view and, to make the problem easier to solve, only hands and faces were used. You can easily see that being able to get a cheap depth field for even a set of objects as limited as hands and faces is going to be very useful for gesture and emotion detection.
The system was trained to evaluate the depth function for each pixel of a set of training data consisting of hands and faces. The good news is that the training generalized well to new subjects and, more surprisingly, to other cameras. You can see it all in action in the following video:
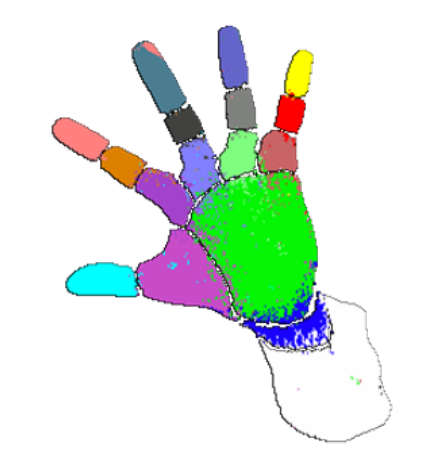
As the video points out, the main limitation of the method is that it only gives good results on surfaces with the trained reflectivity (albedo). However, if it works for skin then there are a lot of applications just waiting for a sensor this cheap. As well as creating a depth map the method was also used to perform hand and face parts identification with good accuracy making it even more useful for gesture and emotion identification.
To make it easy to use and ultra low cost the researchers created new 3D printed backs for a mobile phone that contained the IR filter and the illumination ring. However, you still have to remove the original IR filter from the camera and this probably, no wait - certainly, voids any warranty.
More InformationLearning to be a depth camera for close-range human capture and interaction Learning to be a Depth Camera for Close-Range Human Capture and Interaction, in Journal ACM Transactions on Graphics, July 2014 Related ArticlesLearn More About Intel RealSense Technology Project Tango Tablet Hardware And SDK Announced
To be informed about new articles on I Programmer, install the I Programmer Toolbar, subscribe to the RSS feed, follow us on, Twitter, Facebook, Google+ or Linkedin, or sign up for our weekly newsletter.
Comments
or email your comment to: comments@i-programmer.info |
|||
| Last Updated ( Wednesday, 13 August 2014 ) |