| Solving Archaeological Jigsaw Puzzles |
| Written by David Conrad | |||
| Sunday, 13 January 2019 | |||
|
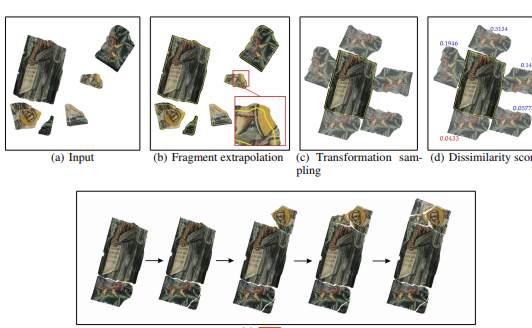
Archaeological artifacts are usually found in bits - and the broken fragments suffer from all sorts of degradation that makes it difficult to reassemble them. Recent research has come up with a novel algorithm for automatic reassembly that performed remarkably well on broken artifacts and frescoes. Jigsaw puzzle solving is a NP-complete problem that crops up in many areas. Israeli researchers Niv Derech and Ayellet Tal of Technion and Ilan Shimshoni of the University of Haifa decided to concentrate on archaeology: because the archaeological domain exposes the limits of current computer vision techniques. Archaeological artifacts are not “clean” and “nicely-behaved”; rather they are broken, eroded, noisy, and ultimately extremely challenging to algorithms that analyze or reassemble them. Therefore, from the point of view of vision, archaeology serves as an extremely challenging application area. The algorithm they proposed is based on four key ideas: First, in order to address fragment abrasion, we propose to extrapolate each fragment prior to reassembly. This reduces the continuity problem (predicting how to 'continue' the fragment) we are facing into a matching problem. Second, we suggest a transformation sampling method, which is based on the notion of configuration space, and is especially tailored to our problem. . Third, at the core of any puzzle solving algorithm lies the question of what makes a good match. We propose a new measure, which takes into account the special characteristics of the domain: the gaps between the pieces, color fading, spurious edges, the fact that the length of the matching boundary varies, and the imprecise transformations. Finally, our placement considers not only the above scores, but also our confidence in the match, which is influenced by the uniqueness of the match and the fragment size.
The researchers evaluated their algorithm on dozens of real archaeological objects from the British Museum and frescoes from churches around the world. They found that it performed remarkably well, successfully reassembling the vast majority of these broken artifacts and frescoes. More details are given in their paper, Solving Archaeological Puzzles, which is available on arXiv. More InformationSolving Archaeological Puzzles Related ArticlesUnshuffling A Square Is NP-Complete To be informed about new articles on I Programmer, sign up for our weekly newsletter, subscribe to the RSS feed and follow us on Twitter, Facebook or Linkedin.
Comments
or email your comment to: comments@i-programmer.info |
|||
| Last Updated ( Sunday, 13 January 2019 ) |