| Custom BitmapSource |
| Written by Administrator | ||||||||||||
| Monday, 03 May 2010 | ||||||||||||
Page 5 of 5
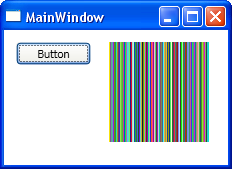
Going furtherThere are lots of additional jobs that need to be completed to make the test card bitmap class work as a complete BitmapSource but the rest is mostly just implementation of the missing methods, properties and events. What is more interesting is to consider problems that arise in implementing more sophisticated custom BitmapSources. No encapsulated BitmapSourceFirst notice that in nearly many case you are going to have to have an encapsulated BitmapSource within your custom class - this is simply the easy way of creating a bitmap that can be presented to the rest of the system. However it isn't essential. As the only time your custom class interacts with the rest of the system is when it passes on the bits that define the bitmap and because this is a transfer to an array in the correct format you only have to provide a method that generates the bit data. For example, our test card class can return the data stored in the byte array rather than using the encapsulated BitmapSource: public override void CopyPixels( Notice that this assumes that the bits byte array is global and accessible and the CopyPixels method isn't general. It only implements the very minimum needed to copy a single stride side chunk of data starting at (0,y). A more complete solution would have to map the sourceRect to the data stored in the byte array. Not difficult but messy. For another, extreem example, let's generate random pixel data everytime CopyPixels is called: public override void CopyPixels( This is particularly simple because all we have to do is fill the pixels array with random numbers - sizes and sourceRectangles are irrelevant! If you try this out you will see a random display
Random pixels If you look at the example image you might be puzzled as to why the random pixels form vertical bars? The reason is that the random number generator is reset for each row of the image using a time dependent seed. Each row is transfered so quickly that the time dependent seed generally doesn't change and so you get a repeat of the pseudo random pattern until the seed does change - when you see an occational tearing of the image. If you want a more reaonable random pattern move the random number generator to be global and create it just once with a time dependent seed. In all of these examples the CopyPixel method has be written to be specific to the data transfer used by the Image control. There is no promise that all data transfers occur in this way so you have to implement all of the CopyPixel methods and in a completely general way. Source properties and chainingAnother common requirement is the need to specify a source property. A source property is simply another BitmapSource instance that you retrieve data from. To do this you make use of the CopyPixels method of choice to transfer the bitmap data in the object specified by the Source to your custom object. In fact you simply implement the mechanism that the Image control uses to get its data. Once you have the represenation of the bits you can arrange for your custom BitmapSource to pass these on to another BitmapSource derived object via its Source property. In this way a chain of Bitmapped sources can be built up. For example, without adding a Source property to our custom bitmap it can still be used as the start of a chain: TestBitmapSource TBS = new
A rescaled test card For more information on how to use transformations see our explorations of the bitmap transform classes. Asynchronous downloadMore advanced BitmapSource classes have to cope with the possibility that the bitmap data wont be available immediately. In this case you have little choice but to implement all of the methods and properties provided by classes such as BitmapImage. The basic idea is that you store a source URI in a suitable property and then either get on with loading it or defer until the pixels are actually needed. For example when a client accesses the bitmap data using CopyPixels your custom class has to check that the data is available and block the thread until it is. Of course blocking the UI thread isn't a good idea and in practice you have implement something more sophisticated using a worker thread to download the data while the UI gets on with its task. This rapidly becomes very complicated and difficult to get right. If possible avoid this task by using the classes provided!
<ASIN:1430219106> <ASIN:1430226501> <ASIN:0735627045> <ASIN:0470499834> <ASIN:0672330318> |
||||||||||||
| Last Updated ( Sunday, 02 May 2010 ) |