| ELIZA Makes a Comeback |
| Written by Sue Gee |
| Sunday, 19 January 2025 |
|
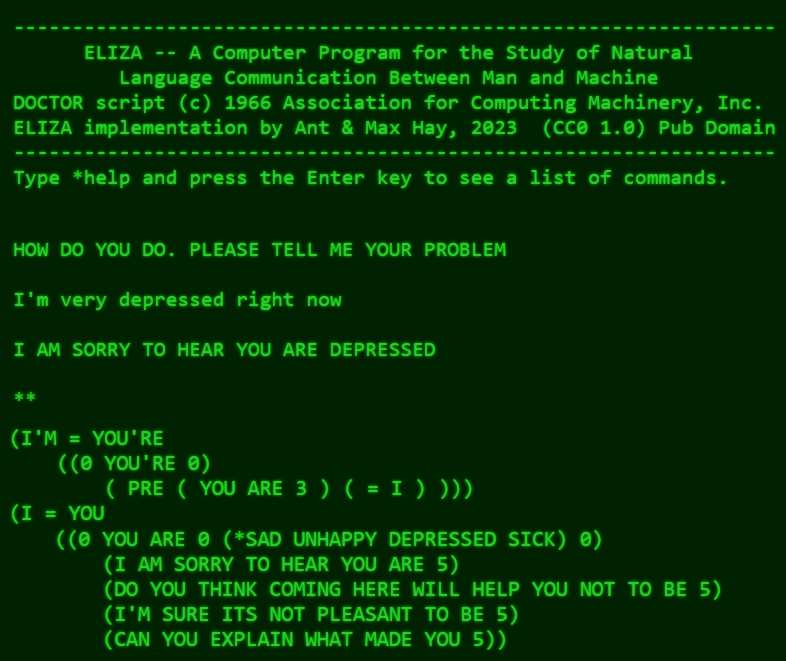
ELIZA was the world's first chatbot, more than 50 years before the term itself was coined. She was the brainchild of Joseph Weizenbaum who wrote the original program in the 1960s at MIT. The original source-code for ELIZA was never published, and remained lost until rediscovered by researchers engaged in the Eliza Archaeology Project. ELIZA was a program designed to simulate conversation by employing a pattern-matching and substitution methodology. It mimics the type of exchange a patient might have with a Rogerian psychotherapist, a type of therapist known for reflecting the patient's words back to them as questions and statements. This technique creates an illusion of understanding and empathy while at the same time encouraging people to talk about themselves. Weizenbaum named his program ELIZA, after Eliza Doolittle, the central character in George Bernard Shaw's play Pygmalion which was popularized by being made into the musical My Fair Lady. However he was deeply disturbed by the extent to which people attributed human-like qualities to his program, becoming a vocal critic of artificial intelligence. In his 1976 book, Computer Power and Human Reason he raised important concerns about the ethical and psychological implications of creating machines that can simulate human interaction. Weizenbaum wrote ELIZA in MAD-SLIP (Michigan Algorithm Decoder Symmetric List Processor), a language he invented specifically for the purpose. However his code was almost immediately copied into LISP, the AI-oriented language from John Mcarthy. With the advent of the early internet, the Lisp version of ELIZA went viral, and the original version became obsolete. Weizenbaum's program was remarkably simple with only 420 lines of code. Over the years there have been many re-implementations including several by members of the I Programmer team. In the 1980's Mike James and Kay Ewbank and I created versions of a program called "Smalltalk" that ran on early home computers, including the Atrari, the BBC Micro and the ZX Spectrum. An open source version of ELIZA designed to be as close as possible to the original, but written in C++ was created by Anthony Hay was made available as part of the Eliza Archaeology Project. Together with his son Max an interactive version was written in JavaScript and inlcuded Eliza Archaeology Project website, see Try Eliza,
It was thought that the original code for Eliza was lost until 2021, when Jeff Shrager, a cognitive scientist at Stanford University, and Myles Crowley, an MIT archivist, found it among Weizenbaum's papers. The paper posted to arxiv describing how they resurrected not only the ELIZA code but also its original operating environment, the first ever multi-user time sharing system, MIT's CTSS running on an IBM 7094. We discovered an original ELIZA printout in Prof. Weizenbaum's archives at MIT, including an early version of the famous DOCTOR script, a nearly complete version of the MAD-SLIP code, and various support functions in MAD and FAP. Here we describe the reanimation of this original ELIZA on a restored CTSS, itself running on an emulated IBM 7094. The entire stack is open source, so that any user of a unix-like OS can run the world's first chatbot on the world's first time-sharing system. After overcoming many problems in restoring the code, the team succeeded in getting ELIZA running in its original environment for the first time in almost 60 years on December 21st 2024. This video provides the authentic experience of interacting with ELIZA. The source code for this is now on GitHub. More InformationRupert Lane, Anthony Hay, Arthur Schwarz, David M. Berry, Jeff Shrager https://github.com/anthay/ELIZA https://github.com/rupertl/eliza-ctss Related ArticlesGPT-4 Doesn't Quite Pass The Turing Test To be informed about new articles on I Programmer, sign up for our weekly newsletter, subscribe to the RSS feed and follow us on Twitter, Facebook or Linkedin.
Comments
or email your comment to: comments@i-programmer.info |
| Last Updated ( Sunday, 19 January 2025 ) |