| Take Stanford's Natural Language Processing with Deep Learning For Free |
| Written by Nikos Vaggalis |
| Friday, 19 November 2021 |
|
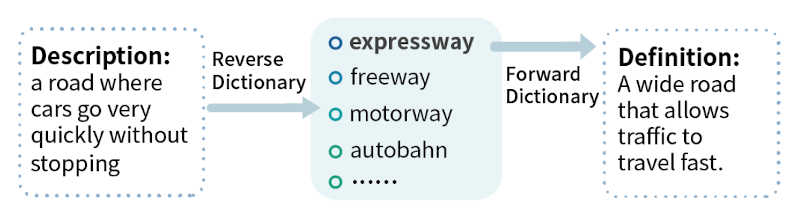
The content of CS224n Natural Language Processing with Deep Learning, a graduate level, one-semester course originally provided to Stanford University Computer Science students, has been made available for free to anyone in a self-paced version. The main focus of CS224n is about investigating the fundamental concepts and ideas in natural language processing (NLP) under a deep learning approach, looking to convey the understanding of both the algorithms available for processing linguistic information as well as the underlying computational properties of natural languages. The material offered is the one of class of 2021, so it is up to date. In any case the concepts don't change, and this course leans heavily towards them. Normally, there would be lot of demanding prerequisites in order to attend and graduate from it: Proficiency in Python College Calculus, Linear Algebra Basic Probability and Statistics Foundations of Machine Learning In the free version, however, you get access to the course's resources and the full YouTube playlist of the recorded lectures without those limitations. That way you get a taste of what it would have been like taking the class as a Stanford student. Especially comforting when you consider that for attending there's a fee of $4,056 - $5,408. Meet main instructor Christopher Manning in this extract from the first lecture: But first of all why get into NLP in the first place? NLP tries to make sense out of textual data, which is much more difficult than doing the same with numerical data. Applications of NLP are everywhere because people communicate almost everything in language: web search, advertising, emails, customer service, language translation, virtual agents, medical reports, etc. Many organizations are looking to integrate NLP into their workflows and products they provide such as translation, speech recognition and chatbots. Sounds like a good career move. An example of such an NLP driven application is the WantWords Reverse Dictionary, which in contrast to a regular (forward) dictionary that provides definitions for query words,returns words semantically matching the query descriptions. What are the use cases of a tool like this?
Without further ado let's take a look at the course's syllabus: 1-Introduction and Word Vectors This syllabus encompasses a number of cutting edge topics:
As far as the course goes, it progresses in incremental difficulty, from word-level and syntactic processing to question answering and machine translation.There's also a final project where students apply a complex neural network model to a large-scale NLP problem. By that time, students' are expected to have gained a firm understanding of implementing, training, debugging, and extending neural network models for a variety of language understanding tasks. This course offering is yet another addition to an increasing catalog of College courses being made available to the general public for free. That's due to the pandemic; probably the only positive outcome out of it. Three other courses that we've examined fall into this category are : Cornell's CS 6120 Advanced Compilers Yann LeCun’s Deep Learning Course Free From NYU Nottingham's University Functional Programming in Haskell Add CS224n Natural Language Processing with Deep Learning to this list. More InformationCS224n: Natural Language Processing with Deep Learning Related Articles Cornell's CS 6120 Advanced Compilers Yann LeCun’s Deep Learning Course Free From NYU Nottingham's University Functional Programming in Haskell
To be informed about new articles on I Programmer, sign up for our weekly newsletter, subscribe to the RSS feed and follow us on Twitter, Facebook or Linkedin.
Comments
or email your comment to: comments@i-programmer.info |
| Last Updated ( Friday, 19 November 2021 ) |