| IBM, Slack, Watson and the Era of Cognitive Computing |
| Written by Nikos Vaggalis | |||
| Monday, 14 November 2016 | |||
|
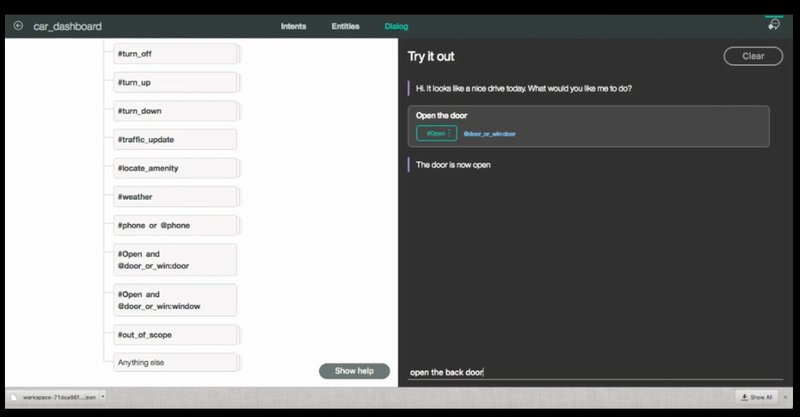
There's a new chapter in the ongoing "Adventures of Watson" which introduces a new character and partner to Watson, going by the name of the Slack Chatbot. It's no secret that IBM considers Watson as its flagship product and is placing all bets on its success. After ensuring its maturity as an end product by outperforming human contenders in the US TV game show Jeopardy and aiding in situations like cancer research, IBM's now looks in expanding Watson's reach into as many practical applications as possible, as demonstrated by its latest $200 million investment in Watson's German IoT headquarters in a move to expand both research as well as client base.So given the recent rise of Cognitive Computing, the partnership in which Watson is to power up Slack's chatbot should come as no surprise. Cognitive Computing is another field of computing in which software starts to perceive the world through learning and experience, just like humans do. As such natural language processing lies at the core of this rising trend, assuming the form of an API available through the Cloud computing platforms and accessible to third parties looking to enhance their applications with advanced cognitive capabilities and AI assistance. The kind of APIs found on IBM's Developer Cloud, range from Language Translation to Natural Language Classification, and Speech to Text transformation to Data analysis. The functionality required for Slack's chat bot, lies encapsulated in the newly introduced Watson Conversation API. Developers plugging into this API can automate spoken or textual interactions between human operators and software applications through the use of natural language. Communicating with machines in a humanly familiar way is an increasing requirement and is met in all sorts of applications, ranging from consumer targeted ones, like Lucida's personal intelligent assistant and Chef Watson's menu suggestions, to ALPHA's military grade AI enabled wingmen. In this demo a human operator is put in the driver's seat of a car's simulator to command the car in textual natural language format. The car not only responds to commands such as 'turn the wind-shield wipers on' and 'turn your lights on' commands, but also engages the driver in a conversation, making him aware of his command's outcome. The good thing with this kind of AI is that despite it utilizing familiar algorithms, it can be nevertheless trained in a vast variety of requirements and scenarios. So Watson's responding to a driver's most frequent requests doesn't get into the way of Conversation's neural network model in getting trained in, say, customer service scenarios. In Slack's case it is trained to interact with a Business's workforce, looking to propel productivity in the workplace. In such a use case, a manager while Slack-chatting with his colleagues, assigns a co-talker the task of travelling to Paris for attending a convention. Without having to leave Slack's interface, that lucky someone, treats Watson as a real assistant and asks: Watson what’s the weather in Paris? getting the appropriate response back. This kind of integration adds to an impressive stack of Slack's B2B integration, hooks that already cover a wide range of needs a business' workforce may have, such as seamless access to GitHub or Mailchimp. To get started with Conversation, you’ll need a cloud Bluemix account, which is free to begin with. After signing in you have to navigate to the 'Watson services', and select the 'Conversation' option. After that you'll be presented with the GUI IDE that you work in for configuring the environment, training the model and implementing the dialogs and intents that Conversation will use in your application. In general terms, the process of utilizing the service can be summarized in the following steps:
All communication between your application and the Conversation API happens through JSON payloads that travel back and forth in the asking and responding phases.
Slackbot's use of the Conversation API marks the beginning of a tight co-operation with IBM in developing advanced cognitive offerings that will firmly establish Slack as a prime platform for business operation. At the end of the day, we should start getting used to frequent news of IBM forming new partnerships as it is through such alliances that cognitive computing's pursuit of the seamless human-computer interaction will be pushed forward, just as the How Will AI Transform Life By 2030? report largely anticipated. IBM is also extending cognitive computing to hobbyists and enthusiasts as demonstrated with TJBot - Using Raspberry Pi With Watson.
More InformationConversation IBM Developer Cloud Conversation Car Demo UI on Github Related Articles$200 Million Investment In IBM Watson TJBot - Using Raspberry Pi With Watson Artificial Intelligence in Pokémons' Service Lucida For Personal Artificial Intelligence How Will AI Transform Life By 2030? Initial Report Achieving Autonomous AI Is Closer Than We Think
To be informed about new articles on I Programmer, sign up for our weekly newsletter,subscribe to the RSS feed and follow us on, Twitter, Facebook, Google+ or Linkedin.
Comments
or email your comment to: comments@i-programmer.info
|
|||
| Last Updated ( Monday, 14 November 2016 ) |