| Data Structures - Trees |
| Written by Mike James | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thursday, 02 November 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Page 3 of 3
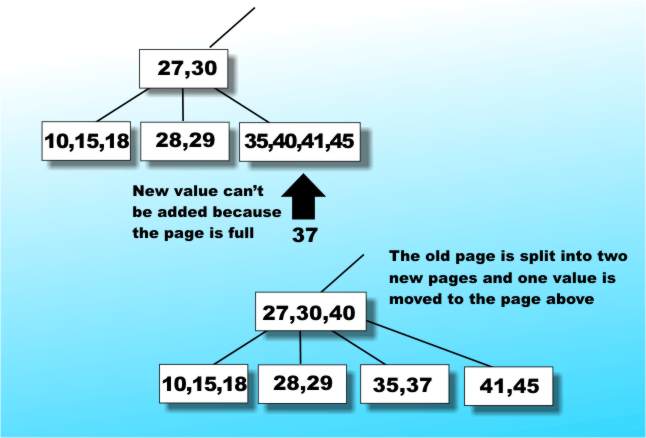
Inserting values into a B-TreeInserting a value into an existing B-Tree so that it remains a valid B-Tree turns out to be amazingly easy for so complex a data structure. If there is still room in the page then insertion really is trivial. The only problem arises if the page is full, i.e. already has 2n items. In this case the full page is split into two new pages at the same level each containing n items and one of the items is inserted into the page above - see Figure 8.
Figure 8: Inserting an item into a B-Tree
Of course there is always the possibility that the item that you have to insert in the page above will need that page to be split and so on, propagating splits perhaps even as far up the tree as the root page. Notice that the splitting operation propagating back to the root is the only way that a B-Tree ever gets any deeper - which is a weird way to grow a tree. You can work out a similar operation for deleting elements from a B-Tree. The advantages of the B-Tree form of index are reasonably obvious:
There are subtle ways of improving the performance of a B-Tree by redistributing items between pages to achieve a better balance but this is icing on the tree. Many database packages proclaim the fact that they are better because they use B-Trees - now you know why. If you need to make use of B-Trees yourself then you can program everything from scratch but there are plenty of B-Tree subroutine libraries that will save you hours of coding and now you understand why you need one and how they work. CreditsI have to admit that my account of B-Trees is based on the one given by Niklaus Wirth in his classic book Algorithms+Data Structure=Programs. If you need a more complete but more abstract approach complete with code fragments then try to get hold of a copy. Alternatively turn to The Algorithm Design Manual or one of other books in the side panel.
Glossary
Related ArticlesData Structures Part I - From Data To Objects Data Structures Part II - Stacks And Trees The LIFO Stack - A Gentle Guide Javascript data structures - the binary tree
Comments
or email your comment to: comments@i-programmer.info To be informed about new articles on I Programmer, sign up for our weekly newsletter, subscribe to the RSS feed and follow us on Twitter, Facebook or Linkedin.
<ASIN:0201657880> <ASIN:0201558025> <ASIN:1848000693> <ASIN:1584504951> |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Last Updated ( Thursday, 02 November 2017 ) |