| Douglas Hartree - Analog Computing With Meccano |
| Written by Mike James | |||
| Monday, 27 March 2017 | |||
|
Douglas Hartree was an English mathematician and physicist who made an important contribution to computing in the era before electronic computers. Using a simple Meccano set he replicated the functionality of the differential analyzer built in the USA by Vannevar Bush. Today is the 120th anniversary of his birth on March 27, 1897. We tend to think that “computer” means “digital computer” but there is another type! Analog computers are all around us and we never give them much thought. A radio, or even a CD player, contains analog circuits that you can consider as making the calculations needed for you to hear the sound. Nowadays the PC tends to take over the task of producing high quality audio by digital means. It is yet another case of digital methods pushing analog ones into history. But not so long ago, the pure analog computer was the preferred tool of anyone wanting to solve a difficult problem. The Meccano ManThis is the story of a man who, after seeing a huge analog computer in the US, went home to the UK and built one using Meccano. He then went on to persuade people that automating calculations was both possible and essential.
Douglas Rayner Hartree The differential analyser is the closest thing you can get to a general purpose analog computer. It can solve differential or integral equations and these are at the core of all of the really successful physical models invented. The principle of an analog computer is to represent the quantities that you are interested in by some physical property and build a machine that simulates the way that the system behaves. For example, a slide rule implements multiplication by representing numbers by lengths. In a slide rule you can see all the advantages and disadvantages of the analog method. A slide rule is fast - it works as fast as you can slide it and in principle it is almost infinitely fast - but it has a limited accuracy due to its mechanical nature.
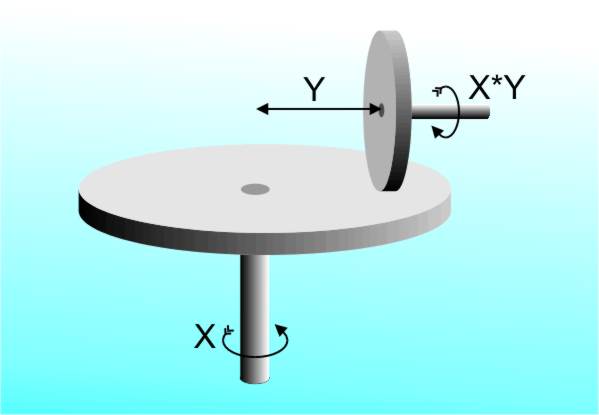
Don’t dismiss analog computers as simply being old fashioned there are problems that they can solve that digital computers find impossibly difficult. For example, the spaghetti computer can find the largest value in a set in one single operation - something that no digital computer can do. How? Simply cut lengths of dried spaghetti proportional to the values and then stand them up - the tallest will stick out of the top of the pile. My second favourite is the string machine - tie lengths of string together to form a model of a network of roads between cities. If you pick up any two “cities” i.e. knots and pull then the length of string pulled taught between them is the shortest path between them. Sounds easy but try to write a program that will find the shortest route between any two cities. The first major differential analyser was built in the USA by Vannevar Bush in 1930. It was huge and driven by big electric motors. Most importantly it was the first working general purpose computer. It could be programmed to do different calculations by moving units about and altering links between them. A differential analyser works by representing the input quantities as the rotation of input shafts. Addition is achieved by rotating the shaft a given amount for each of the input quantities. Multiplication by any given value can easily be achieved by the use of gear wheels but how can you multiply by a variable quantity amount? The answer is you need a gear that can continuously vary its ratio. If you start thinking in terms of altering the number of teeth on a gear wheel then you are guilty of thinking digitally! The real solution is the vertical disc integrator.
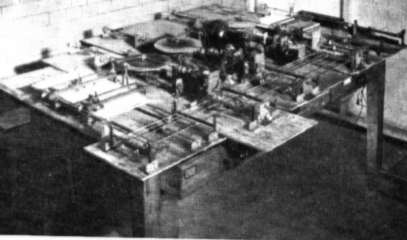
A vertical disc integrator As the vertical wheel is moved in and out from the centre of the horizontal wheel the gear ratio changes. When it is at the centre it is zero and across to the other side the output axle rotates in the other direction so both positive and negative ratios can be represented. Of course all this depends on there being no slip between the two wheels and in practice there is bound to be some slip. The mechanism is called an integrator because if you regard a small turn of the input axle as dx then the output is y dx and varying y while rotating the x axle gives you the integral, i.e. the sum of y dx over the range. Douglas Hartree was a physicist who tackled the very real problem of trying to solve the equations of quantum mechanics. In doing so he started the branch of mathematics that he called numerical analysis. At first he used calculating machines and was renowned for the hours that he would sit turning the handle to churn out results for himself and for other people. Even though he was a wizard with a hand calculator he realised that there had to be better ways and was very interested in automating calculations at a time when the word “computer” applied to a person not a machine! In 1931 he read an account of Bush’s machine and he decided that this was important enough to visit. So in 1934 he arrived in the States with his research student, Arthur Porter. As soon as he saw the gears, wheels and levers of the differential analyser the said that “someone had been enjoying himself with an extra large Meccano set”. When he got back to the UK he did just that. A Meccano set costing £20 was used to build a differential analyser that was within 2% of the accuracy of Bush’s more costly machine.
Hartree's original Meccano computer
It was enough to prove that analog computing was useful and soon a real machine was built at Manchester and established the University's interest in computation that would one day lead to the building of the EDSAC and the series of machines including the MU5. He was also instrumental in the development of LEO, a commerical version of EDSAC developed by J. Lyon & Co, the company well known for its tea rooms, so that the headquarters of LEO Computers was renamed Hartree House after his untimely death in 1958, aged 60. Although Hartree’s name is associated with analog computers, and the Meccano model in particular, this is a little unfair. Later he learned about the ENIAC and wrote about the wider possibilities of automatic computation which included a description of the Harvard Mark 1 as well as pure electronic machines. His enthusiasm for computation was a motivating force in the UK development of electronic machines. On the other hand he didn't envisage computers ever becoming a mass market product. Asked to speculate on the potential demand in the UK for computers he replied: "We have a computer here in Cambridge, one in Manchester and one at the [NPL]. I suppose there ought to be one in Scotland, but that's about all." To be informed about new articles on I Programmer, sign up for our weekly newsletter, subscribe to the RSS feed and follow us on Twitter, Facebook or Linkedin.
Comments
or email your comment to: comments@i-programmer.info <ASIN:9812385770> <ASIN:1884964478> <ASIN:B00008VU7O> <ASIN:B0019H7YVG> <ASIN:0124916503> |
|||
| Last Updated ( Monday, 27 March 2017 ) |