| ACM Grace Murray Hopper Award 2020 |
| Written by Lucy Black | |||
| Friday, 09 July 2021 | |||
|
The 2020 ACM Grace Murray Hopper Award has gone to Shyamnath Gollakota of the University of Washington who is seen as a creative force in his field of wireless computer networks and is now pioneering the Internet of Biological Things.
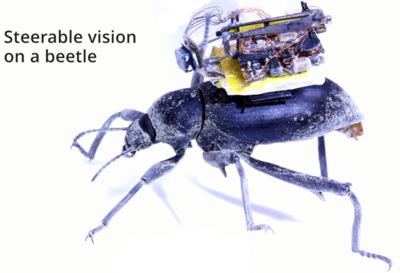
The ACM Grace Murray Hopper Award, one of the four annual ACM Technical Awards, is worth $35,000. Funded by Microsoft. It recognizes a single recent major technical or service contribution made by an individual aged 35 or younger. The citation for the 2020 edition reads: for contributions to the use of wireless signals in creating novel applications, including battery-free communications, health monitoring, gesture recognition, and bio-based wireless sensing. Shyam Gollakota did his undergraduate computer science degree at IIT Madras and his PhD at MIT before becoming According to the University of Washington, as director of the Allen School’s Networks & Mobile Systems Lab, Gollakota has made advances in compact, energy-efficient form factors to expand the Internet of Things (IoT). Among his earliest contributions was ambient backscatter, a groundbreaking technique he pioneered with Allen School colleague and electrical engineering professor Joshua Smith. Backscatter essentially produces power out of thin air by harvesting television, WiFi, and other wireless signals to enable battery-free computation and communication. Gollakota has also tapped into the sensing capabilities of smartphones to develop a series of health screening and monitoring tools. These include a non-invasive app for detecting fluid in the ear and one for detecting obstructive sleep apnea and a smartphone app that employs sonar to monitor a person’s breathing and movements for signs of a potential opioid overdose. With his colleagues he has explored how other smart devices, such as Amazon’s Alexa, can be used for home health monitoring with new smart speaker skills to detect if a person has an irregular heart rhythm or is experiencing a cardiac emergency and also to monitor a baby’s breathing during sleep. In research that I find fascinating, Gollakota and his colleagues have recently embarked on a series of projects that can be described as “living IoT,”. For example, they have outfitted a beetle with a steerable robotic camera that can be used to track moving objects and live-stream images to a smartphone. They have also built insect-sized robots capable of wireless flight; attached sensors to bees to demonstrate a system for wireless data transmission with applications in agriculture and environmental monitoring and developed a lightweight sensor that can be transported to hard-to-reach locations by moths in a step towards creating the Internet of Biological Things. According to the ACM
More InformationRelated ArticlesGrace Hopper Award Goes to CAPTCHA inventor Recognition For NoSQL Pioneers Levesque and Vardi Receive Newell Award Authors of the Dragon Book Win 2020 Turing Award Margaret Martonosi Receives Computer Architecture Award
To be informed about new articles on I Programmer, sign up for our weekly newsletter, subscribe to the RSS feed and follow us on Twitter, Facebook or Linkedin.
Comments
or email your comment to: comments@i-programmer.info |
|||
| Last Updated ( Friday, 09 July 2021 ) |