| The Search For Small Chaotic Circuits |
| Written by Harry Fairhead | |||
| Saturday, 21 October 2017 | |||
|
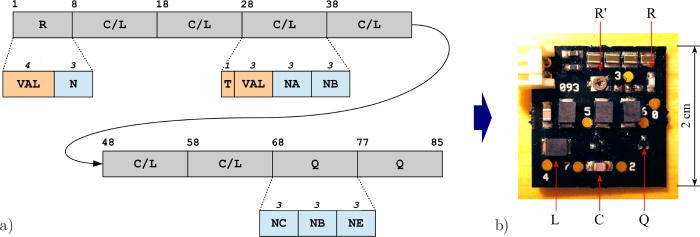
Chaos and complexity seem to go together, but can you make a chaotic circuit with just small number of parts? A supercomputer search suggests that yes you can and chaos is more common than you might expect. Researchers at the Institute of Nuclear Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences (IFJ PAN) in Krakow have been looking into chaos in electronics. In a paper published in the journal Chaos, they have presented 49 new, unusual, chaotic electronic oscillators - not designed but discovered by computer simulations. What they did was code up all of the possible circuits. The structure of the circuits, made up of commercially available components, was mapped as a sequence of 85 bits. In the maximum configuration, the modeled circuits consisted of a power source, two transistors, a resistor and six capacitors or induction coils, connected in a circuit containing eight nodes. The strings of bits thus prepared were then subjected to random modifications. The simulations were made on the Cray XD1 supercomputer. At this point you might think that a genetic algorithm was in order but instead circuits were found by blind search. Given that there were 285 possible circuits you can see why a supercomputer was needed. The circuits were tested using a SPICE simulation for interesting behaviour. The search space was so large that they only managed to test around 2 million circuits, which is a very small slice of the entire space. Of the 2 million 2500 exhibited interesting behaviour. The reason for using a direct search is that past attempts at implementing genetic algorithms on circuits have been less than successful because crossover tended to produce non-functioning circuits. It seems to be difficult to find a representation that works to produce an offspring that has shared characteristics.
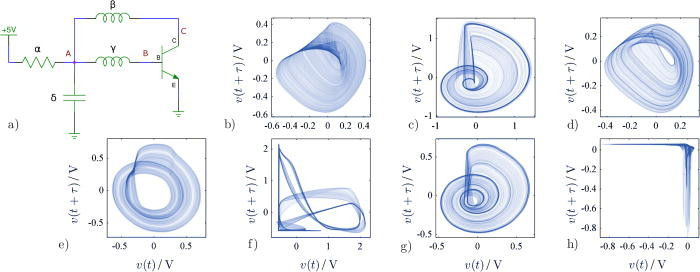
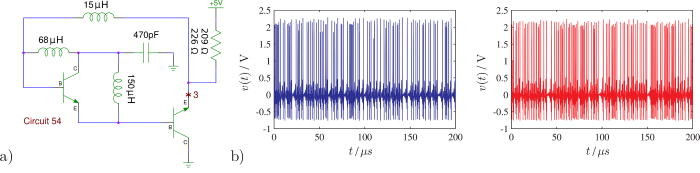
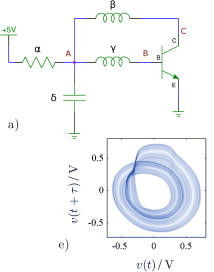
Now we come to an interesting problem. The SPICE simulation wasn't really up to the job of simulating chaotic circuits. This you might expect as the numerical accuracy needed to model chaos is very high. In chaotic systems small changes to the inputs result in large changes to the outputs and this means small errors make the simulation fail. However, when the accuracy was increased it seemed to have little effect on the predictions. As a result there was no choice but to actually build 100 of the most interesting circuits. After some fine tuning, the number of interesting circuits was reduced to 49. The smallest chaotic oscillator used only a single transistor, one capacitor, one resistor and two coils.
Some of the oscillators generated voltage spikes that looked like the sort of thing you measure in biological neural networks:
Before this research only a small number of configurations were known to be chaotic. Now it seems that chaos is not uncommon in small configurations. Transistor-based oscillators have been a ubiquitous staple of electronics for decades, generating periodic signals in disparate applications, e.g., communications, timing, and sound generation. It has been established that small circuits comprising at most few transistors can also generate chaotic signals, which have complex features and are inherently unpredictable, though not random. Among other reasons, such chaotic oscillators have attracted interest for their ability to replicate some phenomena occurring in biological systems when interconnected in networks. However, to date surprisingly little is known about how to obtain them, even whether they represent “unusual” or “special” situations. Here, a large number of transistor-based chaotic oscillators were automatically designed. These circuits do not trivially represent known topologies, or variations thereof, and are therefore “atypical.”
More InformationAtypical transistor-based chaotic oscillators: Design, realization, and diversity Ludovico Minati, Mattia Frasca, Paweł Oświȩcimka, Luca Faes and Stanisław Drożdż Related ArticlesThe Programmer's Guide to Chaos Introduction To The Genetic Algorithm
To be informed about new articles on I Programmer, sign up for our weekly newsletter, subscribe to the RSS feed and follow us on Twitter, Facebook or Linkedin.
Comments
or email your comment to: comments@i-programmer.info |
|||
| Last Updated ( Saturday, 21 October 2017 ) |