| Updated AI Fairness 360 Toolkit Supports R and Scikit-learn |
| Written by Nikos Vaggalis | |||
| Monday, 15 June 2020 | |||
|
AI Fairness 360 is IBM's evolving toolkit which tackles the big problem of discrimination and bias diffusing the machine learning models. It now gets compatibility with Scikit-learn and R. Here at IProgrammer we have examined AI-based bias and discrimination many times in the past both from a technical and societal perspective. Societal wise in "Ethics Guidelines For Trustworthy AI" we've gone through the European Commission's attempt to release a set of guidelines on how to build AIs that can be trusted by society. The verdict was that in order to have "Trustworthy AI", the following three components were deemed necessary:
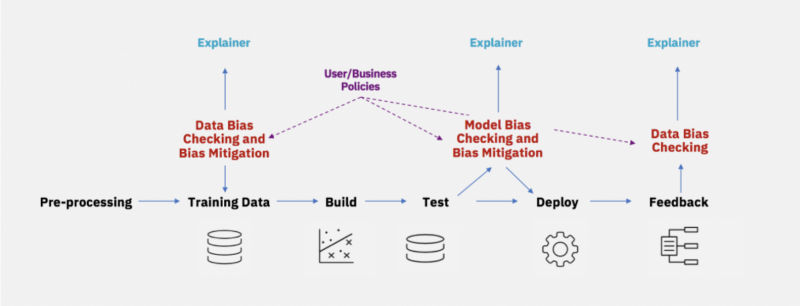
With the ink hardly dry on the pages of the guidelines, a free online course exploring the issues they raise appeared on the openSAP platform. SAP's Creating Trustworthy and Ethical Artificial Intelligence was not just for stakeholders who design, develop, deploy, implement, use, and interact with AI or are affected by it, but also for the wider public. It is underpinned by the value that creating trustworthy and ethical artificial intelligence requires an understanding not only of the technology itself, but also the societal and ethical conditions present. Later on in "How AI Discriminates" we covered “Survival of the Best Fit” an educational game developed by New York University which practically demonstrates how Machine Learning algorithms can make decisions based on bias. The game gives you the role of the CEO of a newly funded company which has secured funding and is in the phase of recruiting personnel using CV Screening and ends by reminding us that: When building automated decision-making systems, we should be asking: what metrics are these decisions based on, and who can we hold accountable? At a purely technical level in "TCAV Explains How AI Reaches A Decision" we've figured out why it is important to understand the inner workings of a neural network and not be treated as a black box: As AI becomes more and more integrated into all aspects of human activity and life there's a pressing need to find a way to peek into its decision making process.This is very important in sectors such as Healthcare, that are critical to humans' wellbeing and justice. This is where Google Brain's scientist Been Kim steps in, with her TCAV (Testing with Concept Activation Vectors) machine-to-human translator tool, a plugin which can be fitted into any NN and understand its reasoning to decide whether we can safely use it or not. That's a lot of build up in order to get to the current news, but I wanted to highlight the importance of the issue and why AIF360 is of great service to the community at large. The official definition of AI Fairness 360 states that it is a toolkit that: can help you examine, report, and mitigate discrimination and bias in machine learning models throughout the AI application lifecycle. Containing over 70 fairness metrics and 10 state-of-the-art bias mitigation algorithms developed by the research community, it is designed to translate algorithmic research from the lab into the actual practice of domains as wide-ranging as finance, human capital management, healthcare, and education. As we encountered in How AI Discriminates and similar to CV screening, AIF360 can be used in domains like in Credit Scoring to detect and mitigate age bias on credit decisions, or in Medical Expenditure where it can detect and mitigate racial bias in Care Management. But these are only the tip of the iceberg; there are many more domains that the toolkit can shed light on by detecting and analyzing the source of bias with its metrics and recommending mitigations with its anti-bias algorithms.
Such algorithms employed are :
And metrics measure :
By cleaning up datasets and mitigating bias, if AIF360 can render the algorithms that play an ever-increasing role in making decisions that affect people's lives fairer, it does not just serve the scientific community but society as a whole. From its inception till now, the toolkit which includes a comprehensive set of metrics for datasets and models, explanations for these metrics and the algorithms to mitigate bias, was available only for Python. Not anymore; R is the new kid on the block introduced with the AI Fairness 360 R package which means the same functionality, metrics and algorithms are now available from within R. But R was not the only one to get support. The new toolkit update also adds compatibility with the Python data science library, Scikit-learn. AIF360 has already been using scikit-learn classifiers with pre-processing or post-processing workflows and the new functionality makes interoperability easier by making the algorithms and metrics between the packages interchangeable. In conclusion, in releasing this versatile toolkit, IBM appears to be taking the issue of bias in datasets very seriously and to be wanting to put its stamp of leadership upon the sector. More InformationAI Fairness 360 Open Source Toolkit The AIF360 team adds compatibility with scikit-learn The AIF360 fairness toolkit is now available for R users Related ArticlesEthics Guidelines For Trustworthy AI SAP's Creating Trustworthy and Ethical Artificial Intelligence TCAV Explains How AI Reaches A Decision To be informed about new articles on I Programmer, sign up for our weekly newsletter, subscribe to the RSS feed and follow us on Twitter, Facebook or Linkedin.
Comments
or email your comment to: comments@i-programmer.info |
|||
| Last Updated ( Monday, 15 June 2020 ) |