| Google's DeepMind Perfects Speech - But There Is More |
| Written by Mike James | |||
| Monday, 12 September 2016 | |||
|
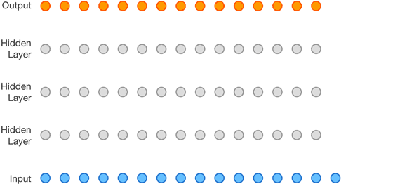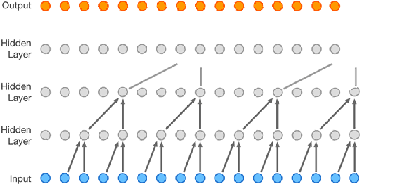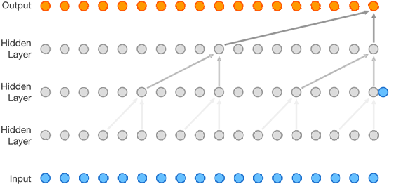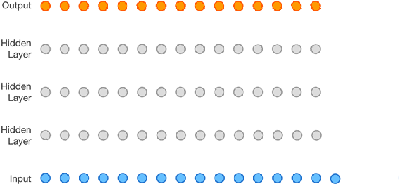
WaveNet is a neural network that generates speech better than ever before. But before you just write this off as another in the long line of neural network successes, this might be more of a breakthrough than just voice. The main part of this story is that Google's AI factory DeepMind has been successful in creating a neural net that does, among other things, speech synthesis better than any software so far. The way that it does this is interesting but the more important point is that the approach might well work with any time varying signal. That is WaveNet is a new approach to time-series prediction and this has lots and lots of applications. Some of the applications are potentially purely practical, such as predicting stock market fluctuations - assuming there is any regularity in the stock market - and some are very fundamental AI. The basic idea is to use a convolutional network, like the sort of image processing networks that have had such success recently, but reduced to one dimension. In this case the data is presented as a time-ordered series and the previous samples are used to predict the current sample. You can see the structure of WaveNet in the animation below:
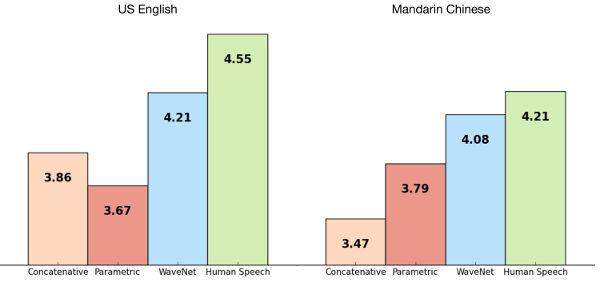
Each time a new sample is added the whole waveform moves up one place. Also notice that the connectivity in each layer is different to give a spaced convolution. This very similar to the Gaussian pyramid of resolutions used in image processing and it allows the network to pick out features at different scales. The network was trained just on speech samples and then run as a generative net by feeding the output back into the input so as to create the next sample. The result is a babbling that sounds very human. It includes speech-like sounds, breathing and other artifacts. The fragments produced correspond to the few milliseconds of samples that the network spans. Next the network was trained with the addition of processed text to provide associations between a symbolic input and the voice output. The result is a network that can do speech synthesis. The network was trained with English and Mandarin and it improved on previous speech synthesis techniques by over 50% as judged by a human panel.
As well as associating text with speech, the identity of different speakers was included and this allows the network to mimic particular human voices. As a final encore, but less interesting than the other results, the network was allowed to listen to some piano music. The result is that it can reproduce a sort of babble of piano sounds and gestures. Fun, but not useful. The point is made in the paper that this ability proves that the network can capture a model of any audio data and the piano music proves it. This is just the tip of the iceberg. There is nothing particularly special about audio data and it seems likely that the same approach would work with any time series. Traditionally time-series models use autoregressive models exactly like the one used for WaveNet. The big difference is that the models have very small numbers of parameters compared to a typical neural network. There seems to be no information provided on the size of network but a Tweet from a DeepMind researcher suggest that it takes 90 minutes of computation to generate just one second of audio using Google's GPU farm. This isn't going to be a practical proposition until the hardware catches up, but knowing hardware this won't take long. WaveNet achieves its performance by having a lot of parameters and using a deep training algorithm. Compared to it traditional autoregressive models are toys. Of course, to allow the training to work, you are going to need a lot of data so perhaps the method isn't so easy to apply to the sorts of data that traditional ARIMA and similar models are used for. But this is supposed to be the age of big data. You can find out more from the paper and you can listen to samples on the DeepMind website.
More InformationWaveNet: A Generative Model for Raw Audio WAVENET: A GENERATIVE MODEL FOR RAW AUDIO Related ArticlesNeural Networks - A Better Speller? Google's DeepMind Demis Hassabis Gives The Strachey Lecture AlphaGo Beats Lee Sedol Final Score 4-1 Google's AI Beats Human Professional Player At Go Google's DeepMind Learns To Play Arcade Games Google Buys Unproven AI Company Deep Learning Researchers To Work For Google Google's Neural Networks See Even Better
To be informed about new articles on I Programmer, sign up for our weekly newsletter, subscribe to the RSS feed and follow us on, Twitter, Facebook, Google+ or Linkedin.
Comments
or email your comment to: comments@i-programmer.info
|
|||
| Last Updated ( Monday, 12 September 2016 ) |